The Water Cycle
The water cycle describes how water continuously moves through our planet via evaporation, condensation, precipitation, ...
RI.4.4RI.4.2
The Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle describes how nitrogen moves through the air, soil, and living organisms. It involves processes like ...
RI.4.4RI.4.2
Determining Earth's Carrying Capacity
Earth's carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of people the planet can support sustainably. This depends on fac...
The Gaia Hypothesis
The Gaia Hypothesis, proposed by James Lovelock, suggests that Earth functions like a living organism, with all its part...
Measuring Carbon Stored in Vegetation
Measuring carbon stored in vegetation is crucial for understanding climate change. Plants absorb CO₂ during photosynthes...
7.RI.7.1
Conserving Forests for Water Supply
Forests play a critical role in maintaining clean water supplies and regulating the water cycle. Conserving upstream for...
7.RI.7.3
Four Ways Forests Affect the Atmosphere
Forests play a vital role in regulating the atmosphere by absorbing CO₂, producing oxygen, cooling temperatures, and imp...
7.RI.7.1
Landform Types Word Sort
This classification activity helps students understand how different landforms are created. Students sort various Earth ...
4-ESS2-2
Weathering Types Word Sort
This classification activity helps students understand different types of weathering processes. Students sort various ex...
4-ESS2-1
Tracking Earth's Water
The 'Tracking Earth's Water' activity guides students to sort 12 water-related words into freshwater and saltwater categ...
Water Around the World
In 'Water Around the World,' students classify 12 water sources into solid and liquid forms, learning about where water ...
Building a Terrain Model
The 'Building a Terrain Model' activity challenges students to classify 12 landscape features and design a model to repr...
Mapping the Landscape
In 'Mapping the Landscape,' students categorize 12 words into landforms and bodies of water to deepen their understandin...
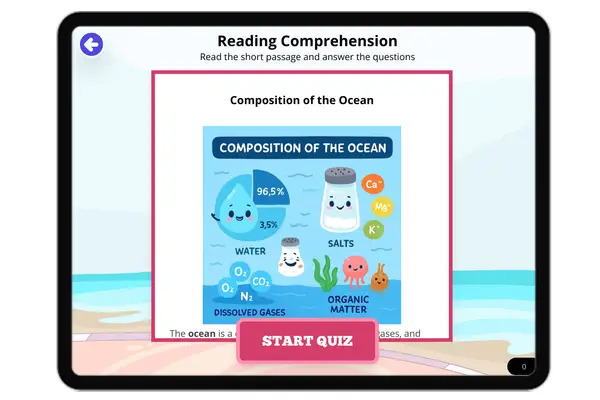
Composition of the Ocean
The ocean is made up of water, dissolved salts, gases, and organic matter. Its composition varies with depth and influen...
RI.5.3
Stream Flow
Stream flow refers to the movement of water in rivers and creeks. It is influenced by precipitation, slope, and human ac...
RI.5.5RI.6.9
The Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is one of the longest rivers in North America, stretching 2,340 miles from Lake Itasca to the Gulf...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
The Mekong River
The Mekong River flows 2,700 miles through six countries in Southeast Asia, ending in the fertile Mekong Delta. It suppo...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Freshwater and Its Sources
Freshwater is a limited resource, with most stored in glaciers and aquifers. Rivers, lakes, and groundwater are key sour...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Difference Between a Rock and a Mineral
Rocks are mixtures of minerals, while minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic solids with a specific composition and...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Convection Currents in the Ocean
Convection currents in the ocean are driven by temperature and density differences. They play a key role in the thermoha...
RI.5.5
Runoff from Precipitation
Runoff from precipitation replenishes rivers and lakes but can cause flooding and pollution. Solutions like rain gardens...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Large Streams of Moving Water
Large streams of moving water, like rivers and creeks, shape landscapes, support ecosystems, and provide freshwater for ...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Topography of the Ocean Floor
This science passage with questions and answers on the ocean floor features diverse landscapes like continental shelves,...
RI.5.3
Porosity and Permeability of Soil and Rock
Porosity and permeability are key properties of soil and rock that affect water movement underground. They influence gro...
RI.5.5RI.6.9
The Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra River originates in the Himalayas and flows 1,800 miles through China, India, and Bangladesh, joining th...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Rare Earth Minerals in Smartphones and Computers
Rare earth minerals are critical for smartphones, computers, and renewable energy. Mining them has environmental impacts...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
What is Transpiration
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere. It cools plants, contributes to hu...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
The Amazon River
The Amazon River is the largest river in the world by discharge volume, stretching 4,000 miles from the Andes Mountains ...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Do All Minerals Have Crystal Structures?
All minerals have a crystalline structure, but not all form visible crystals. The size and shape of crystals depend on f...
RI.5.3RI.6.3RI.7.3
Circulation in the Ocean
Ocean circulation involves the movement of seawater driven by wind, temperature, and salinity. It includes surface curre...
RI.5.3
Surface Ocean Currents
Surface ocean currents are driven by wind and influenced by Earth’s rotation. They transport warm and cold water, regula...
RI.5.3
The Colorado River
The Colorado River stretches 1,450 miles from the Rocky Mountains to the Gulf of California. It carved the Grand Canyon ...
RI.5.5RI.6.9
Types of Plate Boundaries
This science passage explores how geologists use rock formations, fossil distributions, and seafloor structures to ident...
MS-ESS2-3RI.6.1RI.7.4RI.8.2
How Are Metamorphic Rocks Formed?
This science passage explains how metamorphic rocks form through metamorphism, detailing the effects of heat (150°C-1,00...
MS-ESS2-3RI.6.1RI.7.4RI.8.2
Intrusive Igneous Rocks: Formation and Features
This passage explains the formation of intrusive igneous rocks through slow cooling of magma beneath Earth's surface. It...
MS-ESS2-3RI.6.1RI.7.4RI.8.2
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ): Earth's Weather Belt
This science passage explains the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a key equatorial weather system. Covering NGSS ...
MS-ESS2-5MS-ESS2-4RI.6.7
Frost Wedging: How Ice Splits Rock
This passage explains frost wedging as a mechanical weathering process. Aligned with NGSS MS-ESS2-1 (Earth’s systems) a...
MS-ESS2-1MS-ESS2-2RST.6-8.3
Chemical Weathering: The Breakdown of Rocks Through Chemical Reactions
This passage explains chemical weathering processes, aligned with NGSS MS-ESS2-1 (Earth’s systems) and ESS2-2 (surface ...
MS-ESS2-1MS-ESS2-2RST.6-8.4
Limestone Caves: Nature’s Underground Wonders
This passage explains limestone cave formation through carbonation, aligned with NGSS MS-ESS2-1 (Earth’s systems) and L...
MS-ESS2-1LS2.CRST.6-8.7
All About Seismometers
This informational science passage explores seismometers and their role in measuring earthquakes, designed specifically ...
MS-ESS3-2MS-ESS2-3RST.6-8.2
What Is the Difference Between Magma and Lava?
This educational reading passage explains the critical difference between magma and molten rock beneath Earth's surface ...
MS-ESS2-3MS-ESS3-2RST.6-8.4
Obsidian: The Natural Glass Rock
This science reading passage explores obsidian, a volcanic glass that forms when lava cools so rapidly that crystals can...
MS-ESS2-3MS-ESS3-2RST.6-8.4
What Is an Atmospheric Physicist?
This NGSS-aligned middle school science passage introduces students to the role of an atmospheric physicist. It explains...
What Is Space Weather and How Does It Affect the Earth?
This NGSS-aligned science passage for middle school explains what space weather is and how it affects Earth. Students le...
MS-ESS2-2
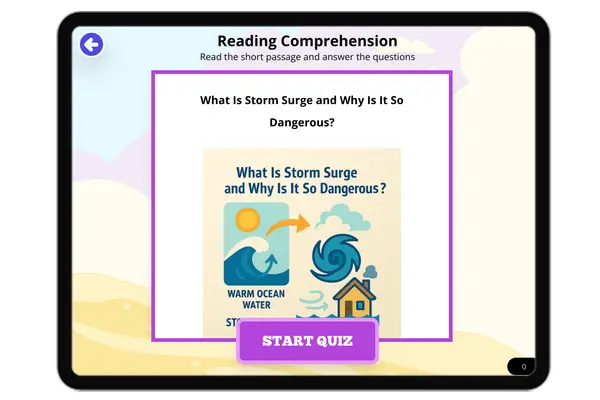
What Is Storm Surge and Why Is It So Dangerous?
This NGSS-aligned reading passage introduces middle school students to the concept of storm surge, a major hazard caused...
What Are Natural Causes That Lead to Increased CO₂ Levels in the Carbon Cycle?
This NGSS-aligned middle school science passage explains natural causes that increase carbon dioxide levels in the carbo...
MS-ESS2-6
What Is a Polar Vortex?
This NGSS-aligned science passage explains the polar vortex, a swirling mass of cold air that stays near Earth’s poles. ...
MS-ESS2-5
What Is the Antarctic Polar Vortex?
This NGSS-aligned science reading passage introduces middle school students to the Antarctic polar vortex—a swirling mas...
MS-ESS2-5
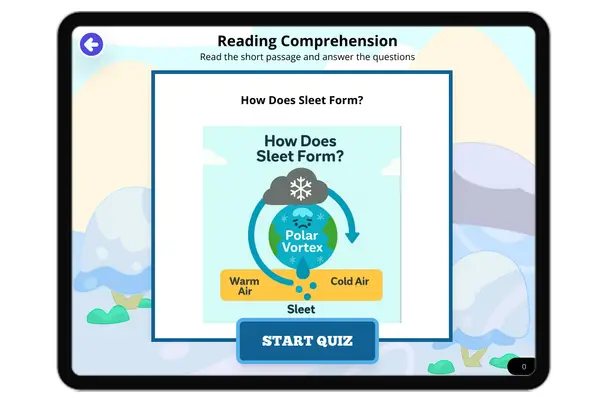
How Does Sleet Form?
This NGSS-aligned science passage explains how sleet forms in the atmosphere. Sleet begins as snow high in the clouds, m...
MS-ESS2-5