Understanding Space Weather

Have you ever heard of space weather? It might sound like the weather forecast for outer space, but it can actually affect us here on Earth!
🌟 Buckle up, young explorers! 🚀 We’re about to embark on an exciting journey into the realm of space weather! Now, you might be thinking, “Wait a minute, weather in space? Is that even a thing?” Well, get ready to have your mind blown because space weather is totally real, and it can have some pretty cool (and sometimes not-so-cool) effects on our planet Earth! 🌍 So, let’s blast off and discover the wonders of this fascinating phenomenon together! 🌠
What is Space Weather?
Space weather refers to the conditions in space that can impact Earth and the technology we use. It is caused by the activity of the Sun, which constantly releases energy in the form of light, heat, and particles. Sometimes, the Sun has giant explosions called solar flares or coronal mass ejections. These events send huge amounts of energy and particles into space, which can cause space weather storms.
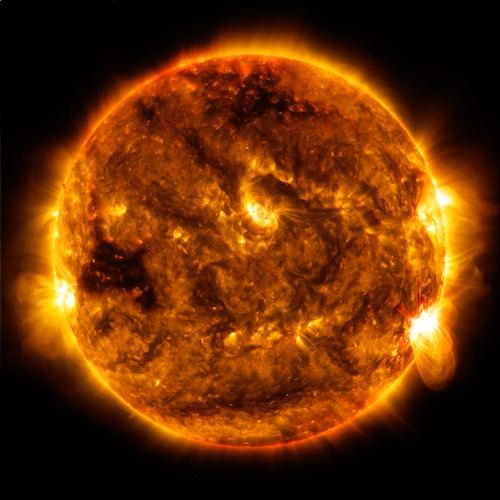

NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of a solar flare – as seen in the bright flash on the lower right limb of the Sun – at 8:12 p.m. EDT on Oct. 1, 2015. The image is a blend of three wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light that have been colorized. Credits: NASA/SDO
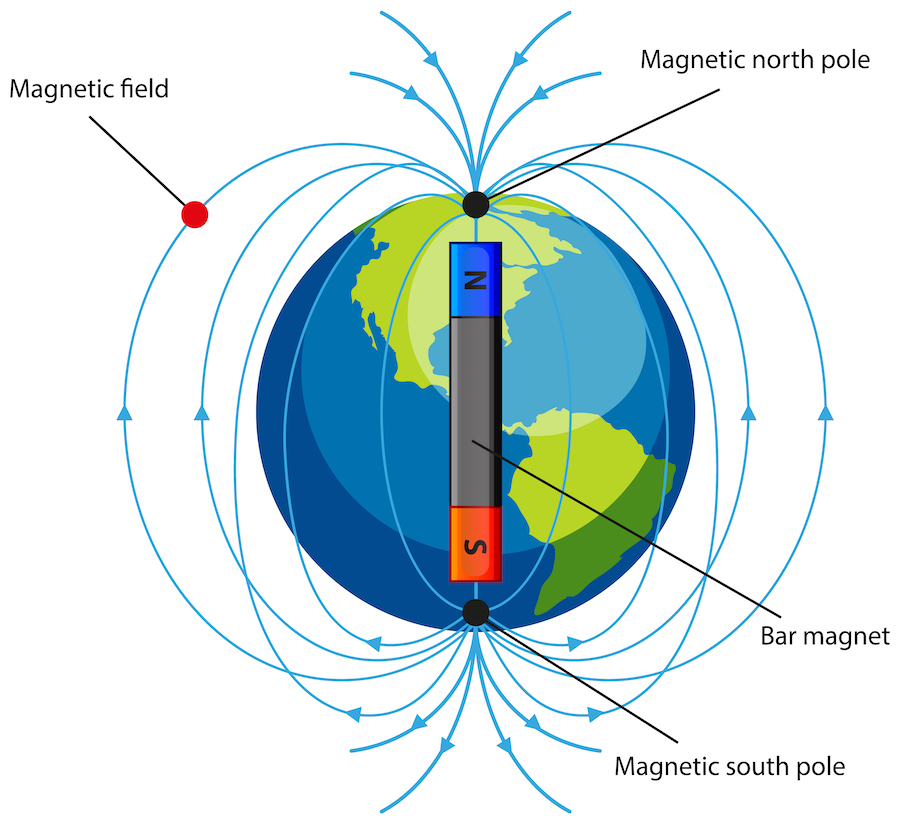
How does Earth’s Magnetosphere Protect Us from Space Weather?
Fortunately, Earth has a special shield called the magnetosphere. It’s like an invisible bubble that surrounds our planet, created by Earth’s magnetic field. When the Sun sends out those high-energy particles, the magnetosphere helps to deflect most of them away from Earth. This protects us from the potentially harmful effects of space weather, like damage to satellites or power grids.
Which Technology Collects Data for Weather, Climate, and Environmental Monitoring from Space?
Scientists use special satellites to study weather in space and its effects on Earth. These satellites are equipped with instruments that can measure things like the Sun’s activity, the speed and direction of solar wind, and changes in Earth’s magnetic field. Some of the most important satellites for this purpose are GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites), which orbit Earth at a fixed point above the equator. They provide continuous monitoring of weather conditions, including space climate, and help scientists predict and prepare for potential impacts.
By understanding weather in space and how it affects our planet, we can work to protect our technology and way of life. It’s amazing to think about how the Sun, which is millions of miles away, can have such a big impact on Earth!
Here are three informational passages along with an accompanying reading comprehension space weather quiz designed for students:
Quiz 1: What is Space Weather?
- Space weather is caused by:
a) The Moon’s gravity
b) The activity of the Sun
c) Earth’s rotation
d) Shooting stars - Solar flares and coronal mass ejections are:
a) Types of planets
b) Giant explosions on the Sun
c) Phases of the Moon
d) Constellations in the night sky - Space weather storms can occur when:
a) The Sun sends out high-energy particles
b) Earth’s magnetosphere disappears
c) Satellites orbit the Earth
d) Astronauts go on spacewalks
Quiz 2: Shielding Earth from Space Weather
- Earth’s magnetosphere is:
a) A type of satellite
b) A visible rainbow around Earth
c) An invisible bubble surrounding Earth
d) A layer of Earth’s atmosphere - The magnetosphere is created by:
a) The Sun’s energy
b) Earth’s gravity
c) Earth’s magnetic field
d) The Moon’s orbit - The magnetosphere protects Earth by:
a) Attracting solar particles
b) Deflecting most solar particles away from Earth
c) Absorbing solar energy
d) Creating auroras in the night sky
Quiz 3: Space-Based Data Collection for Weather
- Scientists use _____ to study space weather and its effects on Earth.
a) Telescopes
b) Weather balloons
c) Satellites
d) Rockets - GOES stands for:
a) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites
b) Global Orbiting Environmental Satellites
c) Geosynchronous Operational Environmental Satellites
d) Geostationary Orbiting Earth Satellites - GOES satellites orbit Earth:
a) At a fixed point above the equator
b) In a figure-eight pattern
c) From north to south
d) Only during space weather storms
Coming soon: Engage with our interactive quizzes on weather in space, Earth’s magnetosphere, and satellite technology! Test your knowledge and receive instant feedback on your comprehension. Stay tuned for this exciting new feature that will make learning about space weather even more fun and rewarding! 🌠💡🎓.



