First Grade Math Vocabulary Every Student Should Know
Math in first grade is all about building a strong foundation for future learning, and mastering first grade math vocabulary is a critical part of that journey. These key terms help young learners grasp concepts, solve problems confidently, and communicate their mathematical thinking.
This guide breaks down essential first grade math vocabulary into clear, easy-to-teach categories, making it simple for parents and teachers to support their students. Whether you’re reinforcing skills at home or planning classroom lessons, these terms align with Common Core and state standards to ensure success.
1. Math Vocabulary Words: Operations & Algebraic Thinking
These terms help students master addition, subtraction, and early problem-solving.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
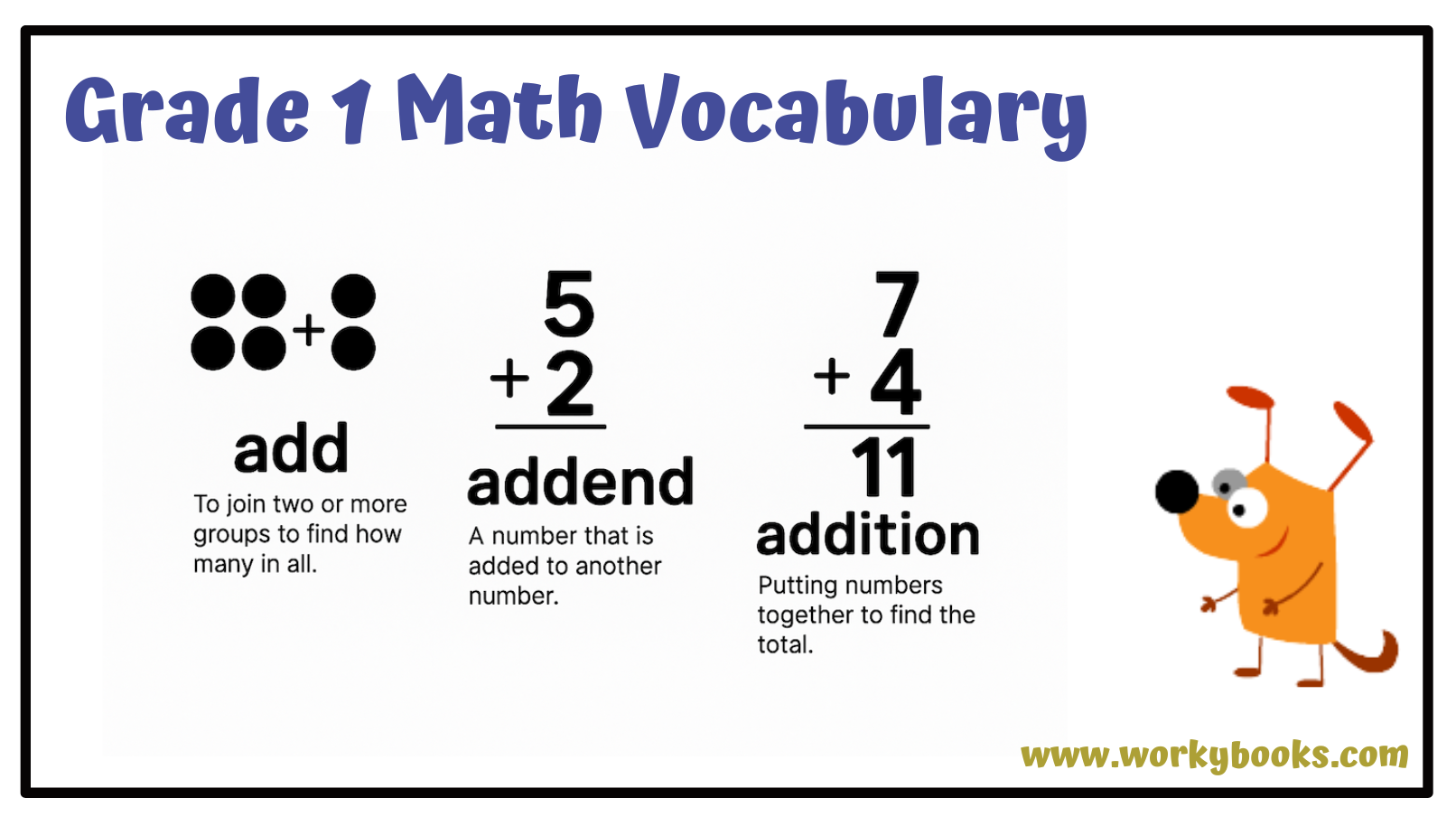
| Add | To join two or more groups to find the total. |
| Addend | A number being added in an addition problem. |
| Addition | Combining numbers to find a total. |
| Associative Property | Grouping addends differently without changing the sum (e.g., (2+3)+4 = 2+(3+4)). |
| Bar Model | A visual tool using bars to represent math problems. |
| Commutative Property | Changing the order of addends doesn’t change the sum (e.g., 5+3 = 3+5). |
| Count Back | Subtracting by counting down (e.g., 7, 6, 5). |
| Count On | Adding by counting up (e.g., 4, 5, 6). |
| Counting | Saying numbers in order. |
| Difference | The answer in a subtraction problem. |
| Doubles | Adding a number to itself (e.g., 6 + 6). |
| Equal | Having the same value. |
| Equation | A math statement showing equality (e.g., 2 + 3 = 5). |
| Equivalent | Different expressions with the same value. |
| Estimate | A close guess (not exact). |
| Even | Numbers divisible by 2 (0, 2, 4, 6…). |
| Fact Family | Related addition/subtraction facts (e.g., 3+4=7, 4+3=7, 7-4=3). |
| Growing Pattern | A pattern that increases predictably (e.g., 2, 4, 6…). |
| Identity Property | Adding zero doesn’t change a number (e.g., 5 + 0 = 5). |
| Minuend | The starting number in subtraction. |
| Minus (–) | The subtraction symbol. |
| Missing Addend | The unknown number in an addition problem (e.g., 3 + __ = 7). |
| Near Doubles | Adding numbers close to doubles (e.g., 6 + 7). |
| Number Bond | A model showing part-whole relationships. |
| Odd | Numbers not divisible by 2 (1, 3, 5…). |
| Ordinal Number | Numbers showing order (1st, 2nd, 3rd…). |
| Pattern | A repeating or growing sequence. |
| Pattern Unit | The repeating part of a pattern. |
| Plus (+) | The addition symbol. |
| Quantity | An amount or number. |
| Related Facts | Math facts using the same numbers. |
| Repeated Addition | Adding the same number multiple times (e.g., 3 + 3 + 3). |
| Repeated Subtraction | Subtracting the same number multiple times. |
| Repeating Pattern | A pattern that cycles (e.g., 🔴, 🔵, 🔴, 🔵). |
| Skip Counting | Counting by 2s, 5s, or 10s. |
| Subtract | To take away from a group. |
| Subtraction | Finding how many are left after taking away. |
| Subtrahend | The number being subtracted. |
| Sum | The answer in an addition problem. |
| Symbol | A math sign (+, –, =, <, >). |
| Number Sentence | A complete math equation (e.g., 4 + 1 = 5). |
| Part-Part-Whole | A model showing how parts make a whole. |
| Join | Combining groups (addition). |
| Separate | Removing a group (subtraction). |
| Think Addition | Using addition to solve subtraction. |
| Comparison | Determining more, less, or equal. |
| Unknown | A missing number in an equation. |
| Benchmark Number | Key reference numbers (e.g., 5, 10, 100). |
Key Concepts:
- Commutative Property – The order of numbers doesn’t change the sum (e.g., 2 + 3 = 3 + 2).
- Associative Property – Numbers can be grouped differently without changing the sum (e.g., (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4)).
- Identity Property – Adding zero to a number doesn’t change it (e.g., 5 + 0 = 5).
2. Math Vocabulary First Grade : Place Value & Number Sense
Key terms for place value, comparing numbers, and working with tens and ones.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Compare | To determine greater, less, or equal. |
| Compose | Putting parts together to make a number. |
| Decompose | Breaking a number into parts. |
| Digit | A single numeral (0-9). |
| Expanded Form | Writing a number by place value (e.g., 43 = 40 + 3). |
| Greater Than (>) | A number is larger than another. |
| Hundreds | The digit in the hundreds place. |
| Less Than (<) | A number is smaller than another. |
| Making Ten | Combining numbers to make 10 (e.g., 7 + 3). |
| Not Equal (≠) | Numbers that are not the same. |
| Number Line | A line showing numbers in order. |
| Ones | The digit in the ones place. |
| Open Number Line | A flexible number line without all marks. |
| Place Value | The value of a digit based on its position. |
| Regroup | Exchanging 10 ones for 1 ten (or vice versa). |
| Standard Form | Writing a number normally (e.g., 57). |
| Ten Frame | A 10-box grid for counting. |
| Tens | The digit in the tens place. |
| Unit Form | Writing numbers by tens and ones (e.g., “3 tens 4 ones”). |
| Word Form | Writing numbers in words (e.g., “twenty-five”). |
| Before | The number just before another (e.g., 5 comes before 6). |
| After | The number just after another. |
| Between | Numbers in the middle of two others. |
| First | The initial position in a sequence. |
| Last | The final position in a sequence. |
| Coin | Money (penny, nickel, dime, quarter). |
| Value | How much something is worth. |
| Two-Digit Number | A number with tens and ones (e.g., 24). |
| Count Forward | Counting upward (1, 2, 3…). |
| Count Backward | Counting downward (10, 9, 8…). |
| Number Word | The word for a number (e.g., “seven”). |
Key Concepts:
- Two-digit numbers (e.g., 24) are made of tens and ones.
- Counting forward and backward helps with number sense.
3. First Grade Math Vocabulary for Measurement & Data
Key terms for measuring, telling time, and understanding graphs.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| a.m. | Time from midnight to noon. |
| Analog Clock | A clock with moving hands. |
| Bar Graph | A chart using bars to compare data. |
| Centimeter (cm) | A metric unit for measuring length. |
| Data | Collected information (numbers, facts). |
| Digital Clock | A clock displaying numbers for time. |
| Dime | A coin worth 10 cents. |
| Dollar | Money worth 100 cents ($1). |
| Feet (ft) | A unit for measuring length (12 inches). |
| Height | How tall something is. |
| Hour | A unit of time (60 minutes). |
| Inches (in) | A small unit for measuring length. |
| Key | The part of a graph explaining symbols. |
| Length | How long something is from end to end. |
| Likely | Something that will probably happen. |
| Line Plot | A graph showing data with X marks. |
| Measure | To find the size, length, or amount. |
| Meter (m) | A metric unit for measuring length. |
| Minute | A unit of time (60 seconds). |
| Nickel | A coin worth 5 cents. |
| p.m. | Time from noon to midnight. |
| Penny | A coin worth 1 cent. |
| Picture Graph | A chart using pictures to show data. |
| Quarter | A coin worth 25 cents. |
| Second | A short unit of time. |
| Table | Organized rows and columns of data. |
| Tally Marks | Marks (丨, 卌) used for counting. |
| Temperature | How hot or cold something is. |
| Time | The measurement of when events happen. |
| Unit | A standard measurement (inch, centimeter). |
| Unlikely | Something that probably won’t happen. |
| Weight | How heavy something is. |
| Width | How wide something is from side to side. |
| Calendar | A chart showing days, weeks, and months. |
| Days of Week | Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, etc. |
| Months of Year | January through December. |
| Seasons | Spring, summer, fall, winter. |
| Graph Title | The name explaining what a graph shows. |
| Longer | Having greater length. |
| Shorter | Having less length. |
| Heavier | Having more weight. |
| Lighter | Having less weight. |
| Capacity | How much a container can hold. |
| Predict | To make an educated guess. |
| Estimate | A close guess (not exact). |
| Compare | To find similarities/differences. |
| Sort | To group by similar attributes. |
Key Concepts:
- Comparing objects (longer/shorter, heavier/lighter).
- Telling time to the hour and half-hour.
4. First Grade Math Vocabulary: Geometry & Shapes Made Simple
Key terms for shapes, fractions, and spatial reasoning.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| 2-D Shapes | Flat shapes (circle, square, triangle). |
| 3-D Shapes | Solid shapes (cube, sphere, cone). |
| Angles | The space between two connecting lines. |
| Attribute | A characteristic (color, size, shape). |
| Circle | A round shape with no corners. |
| Column | A vertical arrangement of objects. |
| Composite Shape | A shape made of two or more shapes. |
| Cone | A 3-D shape with a circular base and point. |
| Congruent | Shapes identical in size and shape. |
| Cube | A 3-D shape with 6 square faces. |
| Cylinder | A 3-D shape with two circular bases. |
| Denominator | The bottom number in a fraction. |
| Edge | Where two faces meet on a 3-D shape. |
| Equal Groups | Groups with the same number of items. |
| Equal Shares | Parts divided fairly (e.g., halves). |
| Face | A flat surface on a 3-D shape. |
| Fourths | Four equal parts (¼, ¾). |
| Fraction | A part of a whole (½, ⅓). |
| Halves | Two equal parts (½). |
| Hexagon | A 6-sided polygon. |
| Parallelogram | A 4-sided shape with opposite sides parallel. |
| Part | A piece of a whole. |
| Pentagon | A 5-sided polygon. |
| Plane Shapes | Flat 2-D shapes. |
| Polygon | A closed shape with straight sides. |
| Prism | A 3-D shape with identical ends. |
| Pyramid | A 3-D shape with a polygon base and triangular sides. |
| Quadrilateral | Any 4-sided shape. |
| Quarters | Four equal parts (¼). |
| Rectangle | A 4-sided shape with 4 right angles. |
| Rectangular Prism | A 3-D shape with 6 rectangular faces. |
| Rhombus | A diamond shape with equal sides. |
| Row | A horizontal arrangement of objects. |
| Sides | The straight edges of a shape. |
| Sixths | Six equal parts (⅙). |
| Solid Shapes | 3-D shapes that take up space. |
| Sphere | A round 3-D shape (like a ball). |
| Square | A 4-sided shape with equal sides and angles. |
| Thirds | Three equal parts (⅓). |
| Trapezoid | A 4-sided shape with one pair of parallel sides. |
| Vertex/Vertices | Corner points where sides meet. |
| Point | An exact location in space. |
| Line | A straight path that goes on forever. |
| Curves | Lines that bend (not straight). |
| Symmetry | When one half mirrors the other. |
| Slide | Moving a shape without turning it. |
| Flip | Reflecting a shape over a line. |
| Turn | Rotating a shape around a point. |
| Build | To create a shape or structure. |
| Trace | To draw around a shape’s outline. |
| Outline | The outer edge of a shape. |
Key Concepts:
- Identifying shapes by their sides and angles.
- Understanding equal parts (halves, quarters).
